Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is caused by the pinching of the median nerve as it passed through the carpal tunnel in the wrist and can result in numbness, tingling, and sometimes pain into the hand affecting the index, 3rd, and thumb-side of the 4th finger. Grip strength weakness may occur (usually later in the process), making dropping of items and fine motor activities, like buttoning shirts, challenging. There are many approaches to the treatment of CTS, of which surgical release of the transverse carpal ligament is the most common and usually recommended by most primary care physicians when tests support the presence of the condition. But, there are more conservative treatment approaches that should be utilized first because they require less recovery time and a common post-surgical complaint is grip weakness. Moreover, the CTS sufferer will lose minimal or no work time when treated with chiropractic approaches, compared with a two to six weeks of lost work time should they undergo surgery, assuming there are no complications. Bottom line, there are no serious side effects to chiropractic management of CTS, so why wouldn’t you try that first since there are potential side effects to the surgical approach?
So, what can you expect when you present for chiropractic management of CTS?
The history process includes how the condition started ("mechanism of injury"), the date of onset, activities that make the condition better and worse, the quality of symptoms, the location of symptoms, the severity (0-10 scale usually), and when the condition is worse (such as night time when sleeping). There are special questionnaires that ask about symptom severity and function loss which are scored and used to track progress during treatment. A pain diagram is completed by the patient that illustrates where the patient has pain, numbness or other symptoms on a map of the body. This is important as frequently in CTS, there are areas in the neck, shoulder, arm, as well as the wrist and hand that may contribute to the patients carpal tunnel symptoms and the successful management of CTS depends on treating ALL areas involved, NOT just the wrist/hand.
The examination of the CTS patient includes observing posture for a forward head position, protracted or rolled forward shoulders, muscle bulk of the arms, and if there is any abnormal spinal curvature or head tilt. The skin is also inspected for lesions, rashes, discoloration, swelling, and hair loss. Next is palpation where we determine if there are any fixated joints and/or trigger points in muscles including the neck, shoulders, arms, or hands. Orthopedic tests are performed where the neck, shoulder, arm, and hand are placed in various positions to see if the symptoms of CTS change. These tests can give your chiropractor clues as to which tissues are contributing to the CTS symptoms. For example, applying thumb pressure over the carpal tunnel will often reproduce the CTS symptoms of numbness and/or pain into the index, 3rd, and thumb half of the 4th finger. When multiple tests reproduce the CTS symptoms, it will let your doctor know which areas require treatment as frequently, a significant contribution to CTS symptoms come from the neck, shoulder, and/or forearm -- NOT JUST the wrist. This is why, in some cases, patients may not have a satisfying result after CTS surgery.
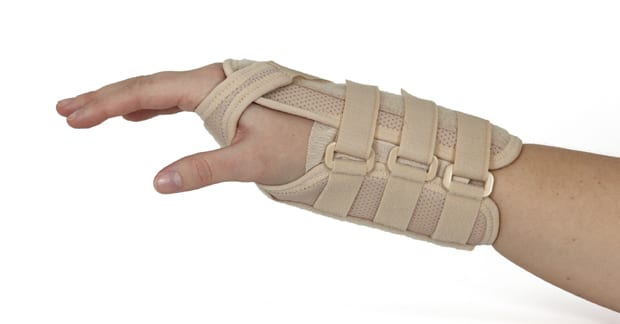
The treatment the CTS patient may expect at the chiropractic office includes manipulation of the neck, shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand. A doctor of chiropractic will often perform muscle release techniques where pressure is applied into the muscles during stretch as well as friction massage. The use of a wrist "cock-up" splint at night is very helpful to reduce the frequency of waking up at night due to hand/finger numbness. Various physical therapy modalities such as low level laser therapy, electrical stimulation, pulsed magnetic stimulation, ultrasound, and others can also be helpful. Also, your doctor may recommend exercises that are extremely helpful and may discuss job modifications to help reduce the repetitive strain that causes and can prolong the condition.